Annotation
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
Annotation Document
apt (Annotation processing tool) 是在编译时,扫描和处理注解的一个构建工具,Java 5 时就已经有了,直到 Java 6 才提供 API 给开发者,apt 的道路实在坎坷,到了 Java 7 又被废弃。现在,该功能由 javac 来实现,我们可以在 javac 编译时源代码额外生成 java 源代码(也可以是其它类型的文件),那么如何处理注解,需要我们了解 AbstractProcessor 这个类。
AbstractProcessor AbstractProcessor 是 javac 扫描和处理注解的关键类,在所有的 ProcessorAPI 中都可以看到它们都继承自 AbstractProcessor ,像下面的代码示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 package cn.septenary.processor;public class MyProcessor extends AbstractProcessor @Override public synchronized void init (ProcessingEnvironment env) @Override public boolean process (Set<? extends TypeElement> annoations, RoundEnvironment env) @Override public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes () @Override public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion ()
init(ProcessingEnvironment env) :javac 会在 Processor 创建时调用并执行的初始化操作,该方法会传入 一个参数 ProcessingEnvironment env ,通过 env 可以访问 Elements、Types、Filer等工具类。process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment env) :它是每个 processor 的主方法,可以在这个方法中扫描和处理注解,并生成新的 java 源代码,通过参数 RoundEnvironment env 可以找到我们想要的某一个被注解的元素getSupportedAnnotationTypes() 指定哪些注解需要注册getSupportedSourceVersion() 指定支持的 java 版本,通常返回 SourceVersion.latestSupported(),如果只想支持到 Java 6 可以返回 SourceVersion.RELEASE_6
在 Java 7 中可以不用重写 getSupportedAnnotationTypes() 和 getSupportedSourceVersion():
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @SupportedSourceVersion(SourceVersion.latestSupported()) @SupportedAnnotationTypes({ // Set of full qullified annotation type names }) public class MyProcessor extends AbstractProcessor @Override public synchronized void init (ProcessingEnvironment env) @Override public boolean process (Set<? extends TypeElement> annoations, RoundEnvironment env)
Register Your Processor 如何让 javac 执行时调用我自定义的 MyProcessor 呢,需要注册自定义的 MyProcessor 来完成
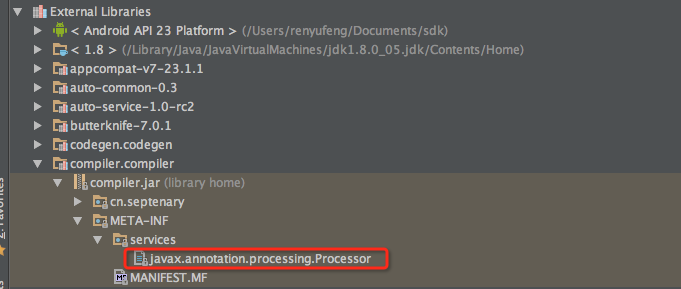
1.MyProcessor 需要打包到 jar 包中,就像其它普通的 .jar 文件一样,这里命名为 MyProcessor.jar MyProcessor.jar 中多了一个特殊的文件:javax.annotation.processing.Processor 它存储在 jar/META-INF/services/ 文件夹下,MyProcessor.jar 的结构是这样的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 MyProcessor.jar
javax.annotation.processing.Processor 文件列出了要注册的 Processor ,每个 Processor 逐行列出
1 2 3 cn.septenary.processor.MyProcessor
构建项目时 javac 自动检测并读取 javax.annotation.processing.Processor 来注册列出来的 Processor
Android Studio 中实现编译时动态生成代码 1.新建工程,分别创建三个模板
app module (Android module)
api module (Java module)
compiler module (Java module)
2.根目录 build.gradle 需要声明依赖插件 android-apt ,它是将 Android Studio 与 annotation processors 结合的一个插件,构建工程时,它会辅助 javac 执行 processor, More
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 buildscript {dependencies {classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'
3.app module Android 模板,使用 android-apt 插件,依赖 api module 和 compiler module
1.使用自定义注解 @MyAnnotation 的类 Bean:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @MyAnnotation public class Bean public String name;public String address;public Bean (String name, String address) this .name = name;this .address = address;@Override public String toString () return StringUtil.createString(this );
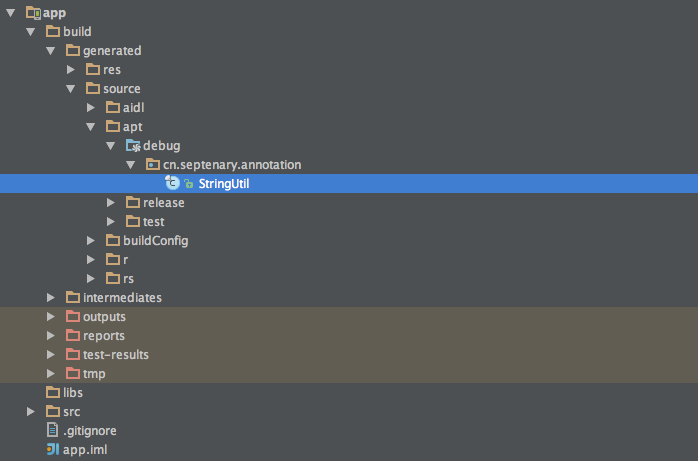
app module 中并没有 StringUtil 这个类,不考虑其他 module ,编写 Bean 中代码时,IDE 会警告找不到 StringUtil这个类,它是在编译时由 javac 和 compiler.jar 自动生成,继续往下看
2.build.gradle :
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt' dependencies {project (':compiler' )
4.lib module 普通的 java 模板,自定义注解 MyAnnotation
build.gradle :
1 2 apply plugin: 'java'
MyAnnotation:
1 2 3 4 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS) @Target(ElementType.TYPE) public @interface MyAnnotation {
5.compiler module 普通的 java 模板
1.自定义注解处理器: MyProcessor
lib ,使用自定义的注解 MyAnnotation,auto-service , 用来自动生成 javax.annotation.processing.Processor 文件, More javapoet ,自动生成代码的工具类库, More
MyProcessor:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 @AutoService(Processor.class) public class MyProcessor extends AbstractProcessor private static final String ANNOTATION = "@" + MyAnnotation.class.getSimpleName();private Messager messager;@Override public synchronized void init (ProcessingEnvironment processingEnv) super .init(processingEnv);@Override public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes () return Collections.singleton(MyAnnotation.class.getCanonicalName());@Override public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion () return SourceVersion.latestSupported();@Override public boolean process (Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) new ArrayList<>();for (Element annotatedElement : roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(MyAnnotation.class)) {if (annotatedElement instanceof TypeElement) {if (!isValidClass(element)) {return true ;try {catch (NoPackageNameException | IOException e) {"Couldn't process class %s: %s" , element, e.getMessage());try {catch (NoPackageNameException | IOException e) {"Couldn't generate class" );for (TypeElement te : annotations) {for (Element e : roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(te)) {"HelloProcessor Printing: " + e.toString());return true ;private AnnotatedClass buildAnnotatedClass (TypeElement typeElement) throws NoPackageNameException, IOException new ArrayList<>();for (Element element : typeElement.getEnclosedElements()) {if (!(element instanceof VariableElement)) {continue ;return new AnnotatedClass(typeElement, variableNames);private void generate (List<AnnotatedClass> list) throws NoPackageNameException, IOException if (list.size() == 0 ) {return ;for (AnnotatedClass annotatedClass : list) {" / " + annotatedClass.typeElement + " / " + Arrays.toString(annotatedClass.variableNames.toArray());0 ).typeElement);new File(System.getProperty("user.home" ) + "/Desktop/" ));private void genHelloWorld () throws IOException "main" ).addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC, Modifier.STATIC).returns(void .class).addParameter(String[].class, "args" ).addStatement("$T.out.println($S)" , System.class, "Hello, JavaPoet!" ).build();"HelloWorld" ).addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC, Modifier.FINAL).addMethod(main).build();"cn.septenary.annotation" , helloWorld).build();new File(System.getProperty("user.home" ) + "/Desktop/Hello" ));private static class AnnotatedClass public final TypeElement typeElement;public final String annotatedClassName;public final List<String> variableNames;public AnnotatedClass (TypeElement typeElement, List<String> variableNames) this .annotatedClassName = typeElement.getSimpleName().toString();this .variableNames = variableNames;this .typeElement = typeElement;public TypeMirror getType () return typeElement.asType();private static class CodeGenerator private static final String CLASS_NAME = "StringUtil" ;public static TypeSpec generateClass (List<AnnotatedClass> classes) for (AnnotatedClass anno : classes) {return builder.build();private static MethodSpec makeCreateStringMethod (AnnotatedClass annotatedClass) new StringBuilder();"return \"%s{\" + " , annotatedClass.annotatedClassName));for (String variableName : annotatedClass.variableNames) {" \"%s='\" + String.valueOf(instance.%s) + \"',\" + " , variableName, variableName));"\"}\"" );return methodBuilder("createString" ).addJavadoc("@return string suitable for {@param instance}'s toString()" ).addModifiers(PUBLIC, STATIC).addParameter(TypeName.get(annotatedClass.getType()), "instance" ).addStatement(builder.toString()).returns(String.class).build();private boolean isPublic (TypeElement element) return element.getModifiers().contains(PUBLIC);private boolean isAbstract (TypeElement element) return element.getModifiers().contains(ABSTRACT);private boolean isValidClass (TypeElement element) if (!isPublic(element)) {"Classes annotated with %s must be public." , ANNOTATION);return false ;if (isAbstract(element)) {"Classes annotated with %s must not be abstract." , ANNOTATION);return false ;return true ;private String getPackageName (Elements elements, TypeElement typeElement) throws NoPackageNameException if (pkg.isUnnamed()) {throw new NoPackageNameException(typeElement);return pkg.getQualifiedName().toString();
build.gradle:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 apply plugin: 'java' dependencies {compile project (':lib' )compile 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc2' compile 'com.squareup:javapoet:1.4.0'
6.构建 api module 生成 api.jar ,供 **lib module ** 和 app module 使用
7.构建 lib module 生成了 complier.jar ,其中关键文件 javax.annotation.processing.Processor 也被自动添加到 jar 包中
8.构建 app module 构建后会看到,IDE 不在警告 TextUtil 找不到的错误了,他的文件被自动生成在:
9.案例源码 Github Source Code
参考链接